Testing of Novel human antibodies against CD99 in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL).
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematopoietic malignancy that accounts for 15% of pediatric and 25% of adult ALL cases. Despite improvements in treatment over the years, approximately 25% of children and 50% of adults still fail to respond to chemotherapy protocols or relapse, thus new treatment strategies are clearly need for T-ALL. Currently the use of antibodies in leukemia is an attractive strategy, given the subtype-specific expression of cell surface antigens.
Recent studies have provided evidences that CD99 receptor triggering with antibodies induces cellular death in CD99 high expressing tumor cells. T-ALLs express high levels of CD99 receptor.
 |
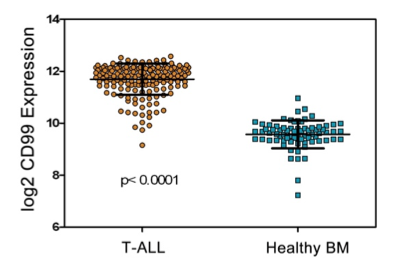 |
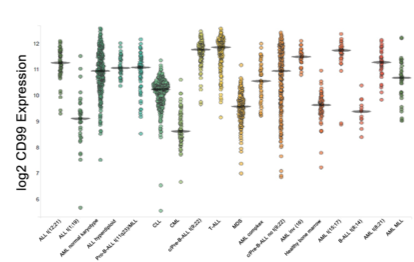
Figure 1: (a) Gene expression of CD99 among 18 MILE study categories (http://servers.binf.ku.dk/bloodspot) (a). CD99 gene expression profile in T-ALL and healthy bone marrow. (b) (Haferlach, Kohlmann et al. 2010) .
CD99 triggering induces cellular death of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) in vitro and exhibits antileukemic activity in AML xenografts. Its role is well characterized in Ewing sarcoma (EWS),where CD99 triggering induced a non-apoptotic form of cell death, known as methousis characterized by dysregulated clearance of vacuoles in the cytoplasm.
In this project, nonimmunogenic recombinant human antibodies to CD99 are evaluated for CD99 triggering in T-ALL settings.
COLLABORATIONS
DIATHEVA SRL
Katia Scotlandi IOR
University of Bologna
Division of Pediatric Oncology of the S.Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital in Bologna
